With the onset of warmer weather, New York’s black bear population will be on the move. The New York State Department of Environmental Conservation (DEC) today issued guidance on how to prevent nuisance bear encounters.
With the onset of warmer weather, New York’s black bear population will be on the move. The New York State Department of Environmental Conservation (DEC) today issued guidance on how to prevent nuisance bear encounters.
Black bears will take advantage of almost any readily available food source, including bird feeders and garbage. To prevent encounters between bears and humans, people should never intentionally feed bears and should take every precaution to discourage bears from seeking out food sources in neighborhoods and other residential areas.
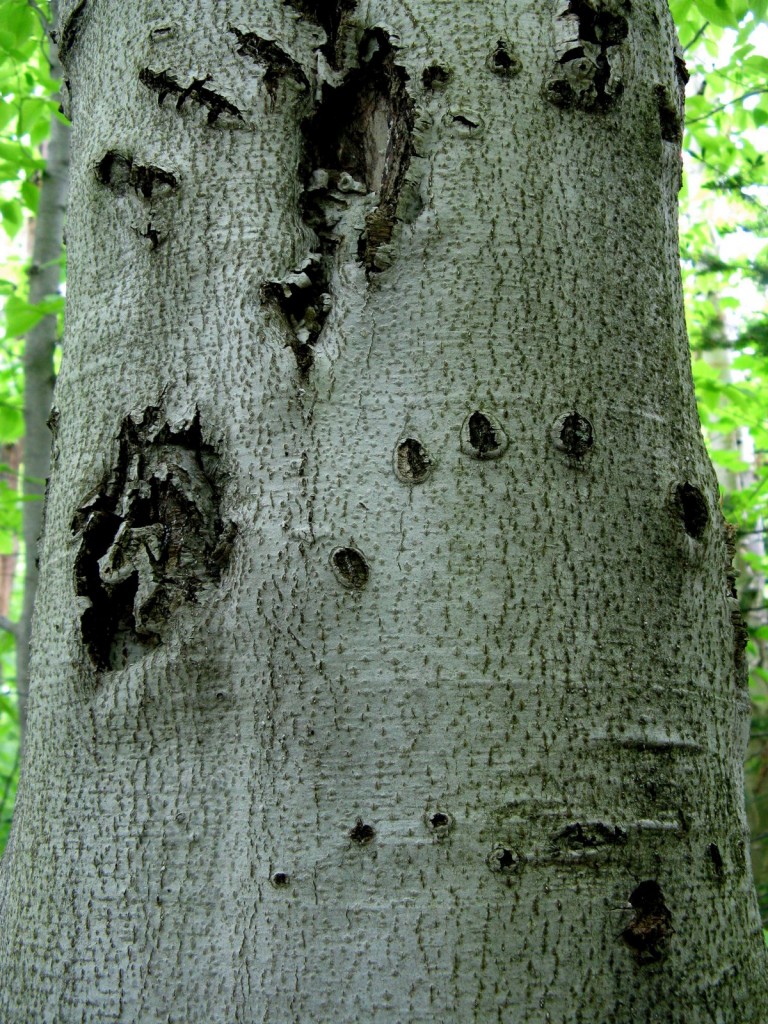
Typically, black bears are timid and will avoid all contact with humans. However, bears will become a nuisance and can cause significant damage if they believe they can obtain an easy meal from bird feeders, garbage cans, dumpsters, barbeque grills, tents, vehicles, out-buildings or houses.
It is not only illegal to intentionally feed bears, it is also illegal to inadvertently feed them. Specifically, after written notice from DEC, the incidental or indirect feeding of bears through food attractants such as garbage, pet food or bird seed is illegal. DEC has the authority to require the removal of these and other food attractants when bears become problematic.
 It is in the best interest of both bears and people for bears to get their food solely from wild sources. Once a bear learns to associate certain structures with food, it can become a serious nuisance to people and a threat to itself. Bears that lose their natural fear of humans are much more likely to be illegally shot, hit by an automobile or destroyed under a DEC nuisance permit. Some studies suggest that when a bear is fed (either directly or indirectly), its life expectancy is cut by as much as 50 percent.
It is in the best interest of both bears and people for bears to get their food solely from wild sources. Once a bear learns to associate certain structures with food, it can become a serious nuisance to people and a threat to itself. Bears that lose their natural fear of humans are much more likely to be illegally shot, hit by an automobile or destroyed under a DEC nuisance permit. Some studies suggest that when a bear is fed (either directly or indirectly), its life expectancy is cut by as much as 50 percent.
Once a bear becomes a problem, DEC is often asked to relocate the bear. Contrary to popular belief, bear relocations are rarely effective at solving the problem. Bears are extremely mobile and have excellent homing abilities. Relocated bears often return to their original capture site or may continue their bad habits at a new location. If the circumstances that led to the original problem are not corrected, other bears will quickly be attracted to the site and the bear/human conflicts will persist.
In addition to being ineffective, bear relocations are extremely time consuming and often dangerous. The heavy door on the bear traps, although not dangerous to bears, presents a potential danger to curious humans and pets. The simplest way to avoid a nuisance encounter is to remove all food sources. Removing the food source will remove the bear.
Because virtually all nuisance bear problems are the result of hungry bears being attracted to human food, pet food, bird food or garbage, these problems can be minimized by taking these simple precautions:
- Never feed bears. It is illegal.
- If you believe that bears are being fed, please report it to DEC.
- Stop feeding birds as soon as the snow melts. Birds do not need supplemental food in the summer, when natural foods are most abundant. Clean up all seed fragments and shells left over from winter feeding as the smell will attract bears.
- Dispose of garbage as frequently as possible and store in a secure building prior to disposal.
- If garbage is picked up at the curb, put the garbage out just before the scheduled pickup or place it in a roadside bear-resistant container. Do not put garbage out the night before pick-up at the curb.
- Clean garbage cans frequently with ammonia.
- Do not burn garbage, it’s illegal and it attracts bears.
- Do not add meat scraps, bones or melon rinds to your compost pile.
- Clean up barbecue grills before night fall, and after they cool down store them inside.
- Feed pets indoors and store pet food indoors. If pets must be fed outdoors, take in all uneaten food and dishes before dark.
- Turn off kitchen exhaust fans that vent to the outside whenever possible.
- When camping, keep food out of sight and secured in the trunk of a hard topped, locked vehicle if one is available. If a vehicle is not available, hang food and garbage from a tree at least eight feet off the ground. Keep picnic tables, utensils, fireplaces and the surrounding areas clean.
To learn more about black bears, look for DEC’s DVD Living with New York Black Bears at your public library or visit DEC’s website: Black Bear
Everyone is asked to respect bears as wild animals — from a distance. For more information about bears in your area, contact the nearest regional DEC office. For a list of regional offices, visit http://www.dec.ny.gov/about/558.html on the DEC website.