Record Takes Again In the Southern Zone
 New York bear hunters took 1,358 black bears during the 2013 hunting seasons, making last year the second highest bear harvest on record in New York, Department of Environmental Conservation (DEC) Commissioner Joe Martens announced today.
New York bear hunters took 1,358 black bears during the 2013 hunting seasons, making last year the second highest bear harvest on record in New York, Department of Environmental Conservation (DEC) Commissioner Joe Martens announced today.
“New York has excellent bear habitat and vast, accessible public lands that offer exciting opportunities for bear hunting,” said Commissioner Martens. “With abundant natural foods this past year, bears were in great condition, and we heard of several hunters who took bears weighing more than 500 pounds dressed. Under New York’s Open for Fishing and Hunting, our Fish and Wildlife Programs are being enhanced and our hunting and fishing licenses are streamlined to ensure increased opportunities for recreational in this state.”
 Regionally, bear hunters took a record 636 bears from the Southeastern bear hunting area and a near record 342 bears (2nd highest take) from the Central-Western bear hunting area. These high harvests reflect that bear populations have increased over the past decade. In addition, an abundance of hard mast (e.g., acorns and other nuts) kept many bears actively feeding later into the fall and available for harvest through the duration of the regular firearms season. Hunters took 224 bears in the Central-Western area and 431 bears in the Southeastern area during the regular firearms season. Bear populations in these ranges are in need of higher harvest rates in coming years in order to stabilize population growth generally and reduce populations in the Catskill region.
Regionally, bear hunters took a record 636 bears from the Southeastern bear hunting area and a near record 342 bears (2nd highest take) from the Central-Western bear hunting area. These high harvests reflect that bear populations have increased over the past decade. In addition, an abundance of hard mast (e.g., acorns and other nuts) kept many bears actively feeding later into the fall and available for harvest through the duration of the regular firearms season. Hunters took 224 bears in the Central-Western area and 431 bears in the Southeastern area during the regular firearms season. Bear populations in these ranges are in need of higher harvest rates in coming years in order to stabilize population growth generally and reduce populations in the Catskill region.
2013 Black Bear Harvest Comparison
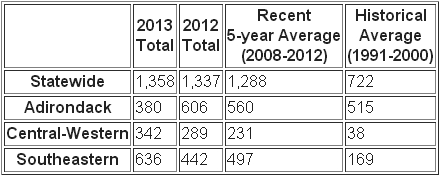
In the Adirondack bear hunting area, hunters took a total of 380 bears, fewer than the recent 5-year average. However, Adirondack bear harvest is the tale of two seasons. Bear harvest during the early bear season, which runs from mid-September through mid-October, is strongly influenced by availability of soft mast (e.g., apples, cherries and berries), and harvests tend to be poor during years with abundant soft mast like the 2013 year. Early season only accounted for 84 bears taken, approximately 65 percent below average. In contrast, hunters did well during the regular season, taking 246 bears, about 13 percent greater than average.
A complete summary of the 2013 bear harvest with results by county, town, and Wildlife Management Unit is available on the DEC website.
NYS Black Bear Management Plan
In January, DEC released a draft black bear management plan for public review and comment. The plan describes DEC’s approach to bear management which includes population management through regulated hunting, mitigation of human-bear conflicts, and technical guidance and outreach to the public about bears and conflict avoidance. The plan proposed several changes to bear hunting, including expanding the area open to bear hunting to encompass all of upstate New York and establishing a supplemental firearms season in September for bears in the Catskill and lower Hudson Valley region. DEC is reviewing the comments received on the plan and anticipates publishing a final version of the plan this spring. See Black Bear Management to review the draft plan.
NYS Black Bear Cooperator Patch Program
Hunters play a pivotal role in bear management through reporting their bear harvests, and many hunters also submit a tooth sample from their bear for DEC to determine the age of harvested bears. For all hunters who report their harvest and submit a tooth, 680 hunters in 2013, DEC provides a NYS Black Bear Cooperator Patch and a letter informing them of their bear’s age. DEC is still processing tooth submissions from 2013, but we anticipate hunters will receive their patch by September 2014.
Governor Cuomo’s NY Open for Fishing and Hunting Initiative is an effort to improve recreational opportunities for sportsmen and women and to boost tourism activities throughout the state. This initiative includes streamlining fishing and hunting licenses, reducing license fees, improving access for fishing and increasing hunting opportunities in New York State.
In support of this initiative, this year’s budget includes $6 million in NY Works funding to support creating 50 new land and water access projects to connect hunters, anglers, bird watchers and others who enjoy the outdoors to more than 380,000 acres of existing state and easement lands that have gone largely untapped until now. These 50 new access projects include building new boat launches, installing new hunting blinds and building new trails and parking areas. In addition, the 2014-15 budget includes $4 million to repair the state’s fish hatcheries; and renews and allows expanded use of crossbows for hunting in New York State.
This year’s budget also reduces short-term fishing licenses fees; increases the number of authorized statewide free fishing days to eight from two; authorizes DEC to offer 10 days of promotional prices for hunting, fishing and trapping licenses; and authorizes free Adventure Plates for new lifetime license holders, discounted Adventure Plates for existing lifetime license holders and regular fee Adventure Plates for annual license holders.







